Introduction
The “quad zygoma” concept involves the insertion of four zygomatic implants, with adequate anteroposterior spread and correct inclination for the distribution of forces, as a means of rehabilitating patients presenting with insufficient bone height in the anterior and posterior maxilla. The technique has been clinically tested, using protocols for immediate function, with promising short- and long-term results 2,3,4.
It is widely accepted among the medical community that the use of four zygomatic implants with an immediate loading protocol is a viable option for rehabilitating patients with severe maxillary atrophy. This approach offers an excellent alternative to bone grafting procedures 4.
Initial situation
Description of the patient:
A 74-year-old male patient was referred to our department by another center and presented with a failure of a fixed bridge in the maxilla. Six implants had initially been placed in 2010, three of which were removed over the next 10 years and three of which were still present. The patient became aware of the problem three years ago (aggressive peri-implantitis) and since then has been looking for a predictable replacement solution. (FIGS. 1-4)
- Fig 1. OPG showing extremely resorbed maxilla and three failing implants.
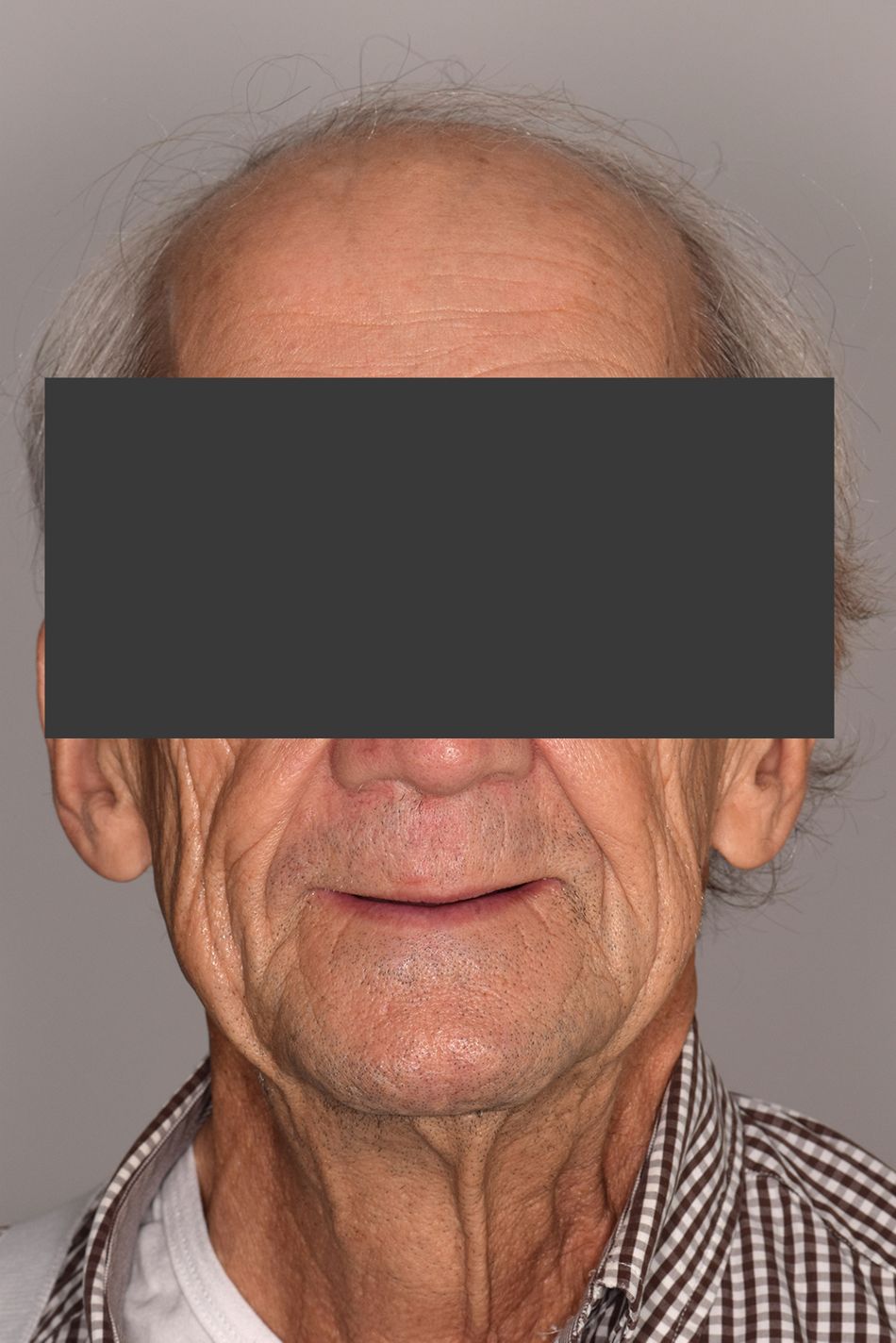
- Fig 2. Frontal view of the face of the patient
- Fig 3. Profile view of the patient
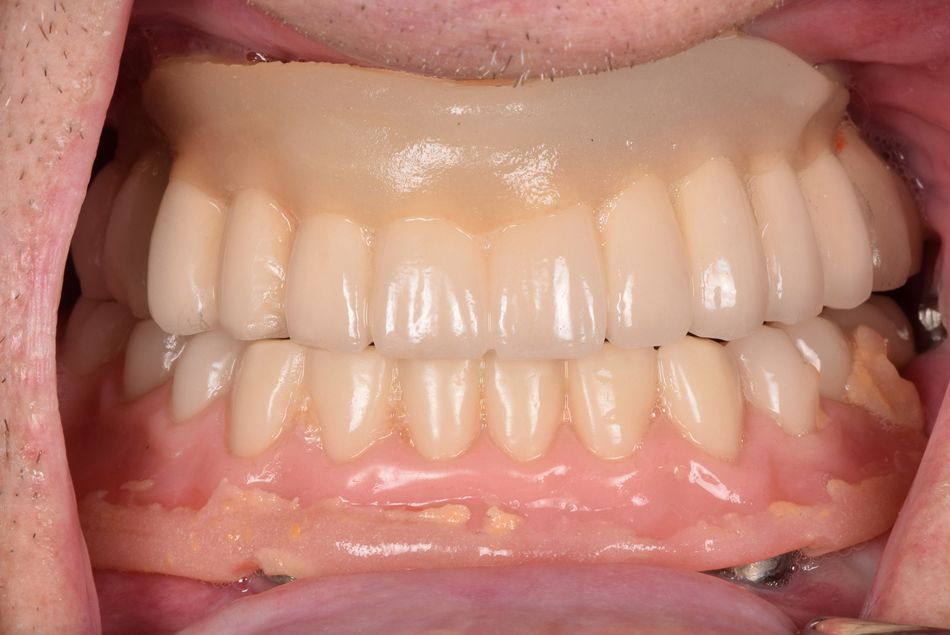
- Fig 4. Preoperative occlusal view showing denture for the upper jaw and fixed bridge on 4 implants for the lower jaw.
Treatment planning
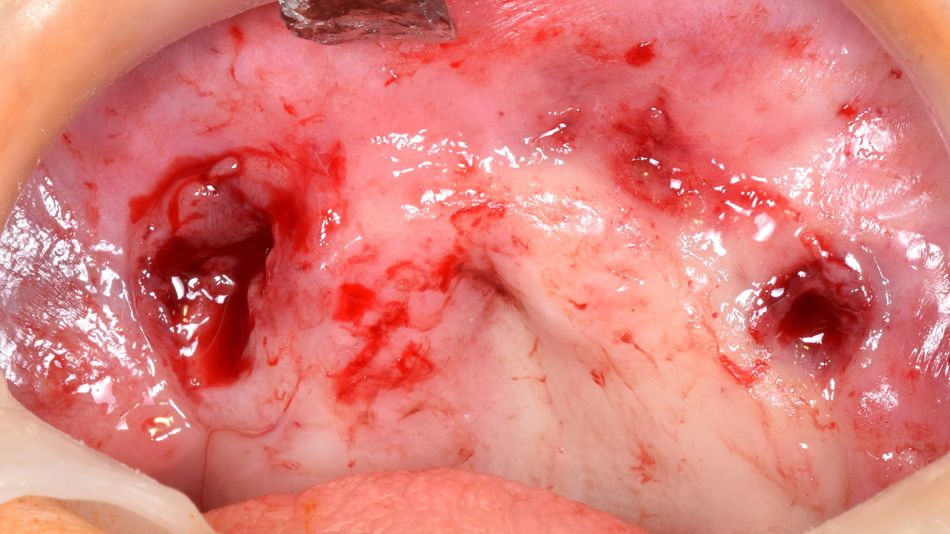
After the three failing implants (FIG. 5) were removed, the surgical planning was conducted digitally using dedicated planning software. (FIG. 6)
- Fig 5. Intraoral view after removing three failing implants.
- Fig 6. Planning of the surgery, using 4 zygomatic implants, 2 on each side.
The planned treatment sequence was as follows:
- Decision to use four Straumann zygomatic implants inserted in:
- Position 23: 45 mm Zaga Round implant
- Position 26: 37.5 mm Zaga Flat implant
- Position 13: 47.5 mm Zaga Round implant
- Position 16: 37.5 mm Zaga Flat implant
In the present case, all the zygomatic implants were guided into the lateral wall of the maxilla by means of a channel osteotomy, because the alveolar ridge was almost non-existent. The apical parts of all implants were anchored in the outer cortical part of the zygomatic bone.
- Immediate loading protocol
After impressions were taken, a provisional acrylic fixed bridge was designed and screwed onto the implant abutments.
Surgical procedure
Surgical technique
The surgical technique has been described by several authors 3.
Intravenous sedation or general anesthesia is typically used, with intraoral infiltrative local anesthesia in the surgical area, facilitating hemostasis and reducing the amount of analgesia required.
In order to control the risk of infections, particularly in the sinus area, the following antibiotic protocol was applied: one day before surgery, and for 10 days post-operatively, 750 mg amoxicillin and 125 mg clavulanic acid, three times a day). The patient was draped such that the sterile surgical area was clearly identifiable and the infraorbital rim, lateral orbital rim, and body of the zygoma could be palpated by the surgeon during the procedure.
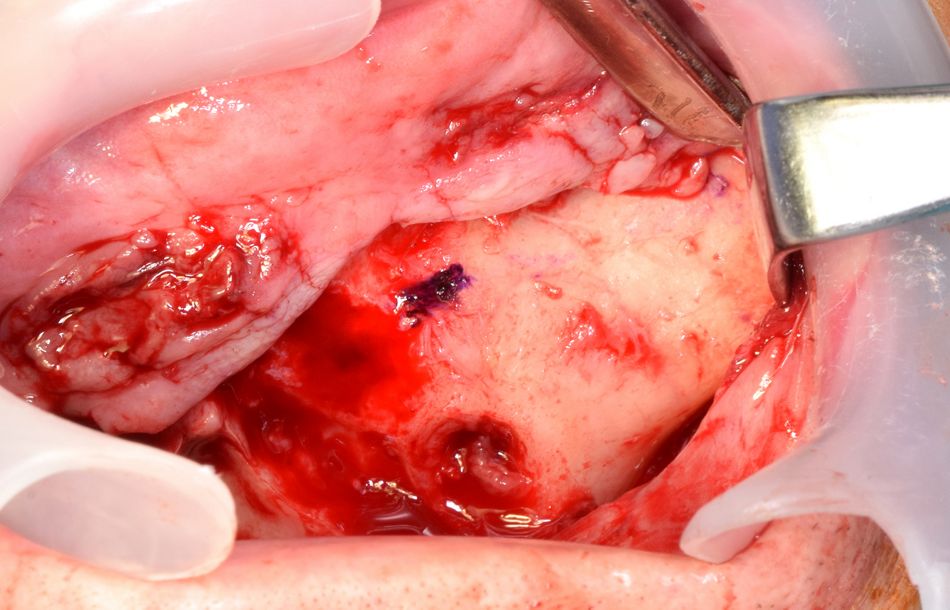
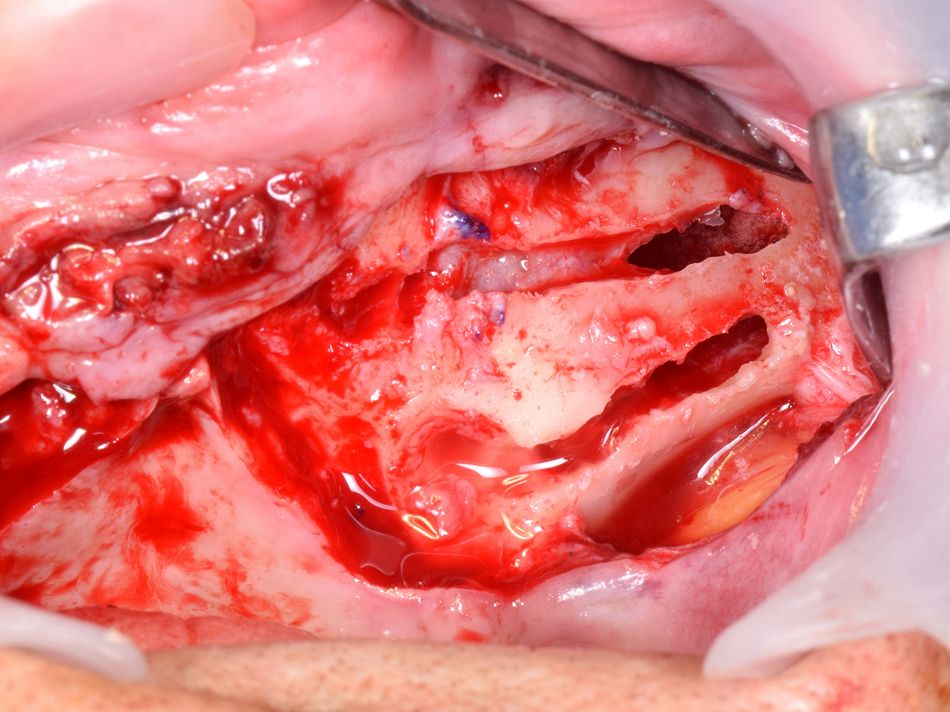
A full-thickness palatal incision was made on the alveolar ridge from first molar to first molar. This type of palatal incision ensures that a good width of keratinized tissue surrounds the implants labially/buccally after suturing. Distal vertical releasing incisions were made bilaterally to enable good visualization of the surgical site after the mucoperiosteal flap was raised. Subperiosteal dissection was carried out in a superior direction following the path of the zygomatic buttress to the frontozygomatic notch (FIG. 7). It is critical to visualize the following anatomical structures:
- the maxilla, from the piriform apertures up to, and including, the zygomatic buttress
- the infraorbital foramen
- the malar bone
- the palate adjacent to the incision
- Fig 7. View after degloving lateral wall of the maxilla, up to the zygoma bone (left side). Positioning of the anterior implant is pointed.
Special care was taken to identify, preserve, and protect the infraorbital neurovascular bundle. Once the surgical field was appropriately exposed, a retractor was placed in the frontozygomatic notch to allow for good visualization of the malar bone during osteotomy preparation. This also enables the surgeon to define and assess the path of the osteotomy preparation.
The positioning of the implants considers the anatomy of the body of the zygoma and the maxilla. The goal is to place two zygoma implants into a finite space with an appropriate prosthetic emergence profile and as mid-crestal as possible. A cadaver study assessing the accuracy of drilling guides demonstrated that two implants can generally be placed at the level of the zygoma bone, given the height and width measurements of a typical malar bone 5.
The anterior implants were inserted first and emerged at the level of the canines or lateral incisors. The posterior implants emerged in the molar or premolar areas. The implants must be evenly distributed in the zygomatic bone and, ideally, positioned so that they are spatially apart from each other.
Following the soft tissue dissection, different osteotomy techniques to place the zygoma implants were described 3. In this particular case, in order to adapt the implants to the anatomy of the patient and to allocate the implant at the lateral wall of the maxilla a channel osteotomy was preferred for each implant (FIG. 8). Special attention was paid to preserving the integrity of the Schneiderian membrane.
- Fig 8. Preparation of the osteotomies for the placement of the implants. A diamond bur or piezoelectric is used to prepare 2 “Chanel” osteotomies in the lateral wall of the maxilla. A 2,9 diameter burr is used to prepare de osteotomies at the level of the zygoma bone.
Drilling of the zygoma bone started with a 2.9 mm round drill and pursued with 2.9 mm twist drill. This diameter suits to the anatomy of a vast majority of patients.
Abundant irrigation is crucial at the alveolar crest but also, equally importantly, at the apex of the implant in the malar bone to avoid overheating. During the osteotomy, regular extra-oral palpation of the malar bone is prudent.
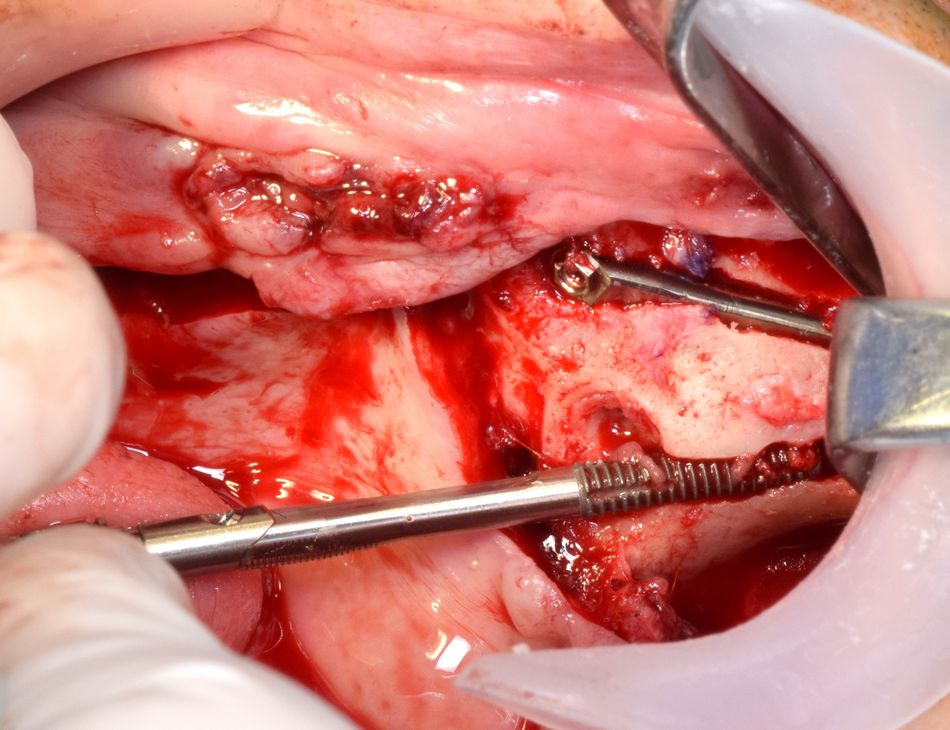
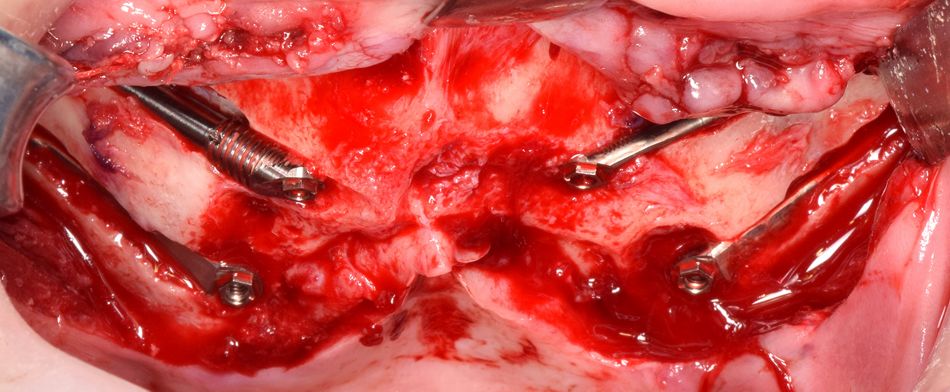
Insertion of the implants was carried out (FIGS. 9-10), and the same procedure was repeated on the other side (FIGS. 11-13).
- Fig 9. Anterior implant in place. Placement of the posterior implant.
- Fig 10. Both implants in place (Zygoma Zaga round and Zygoma Zaga flat).
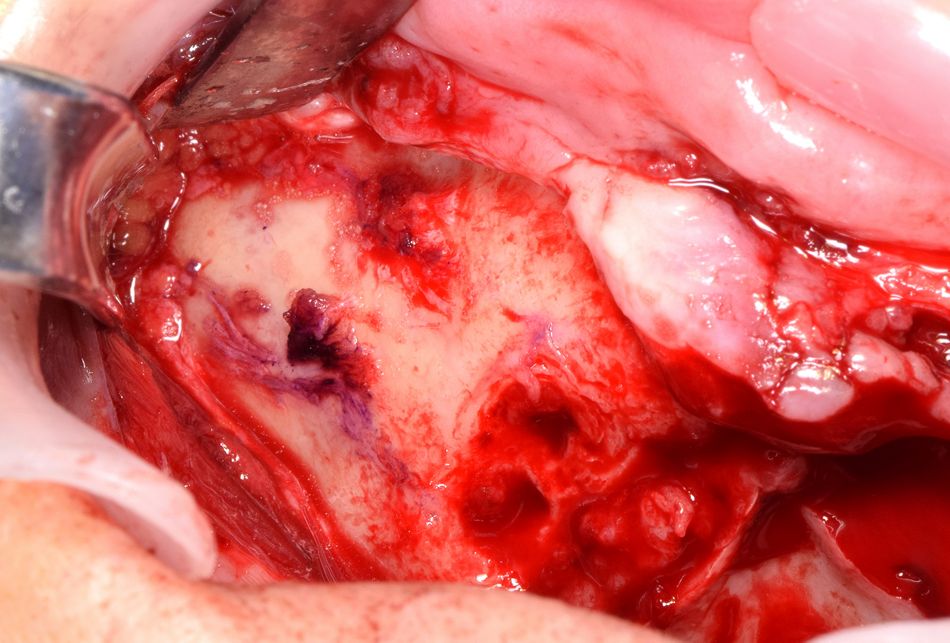
- Fig 11. View of the lateral wall of the maxilla, up to the zygoma bone after degloving (right side). Positioning of the anterior implant is pointed.
- Fig 12. Preparation of the osteotomies for the placement of the implants. A diamond bur or piezoelectric is used to prepare 2 “Chanel” osteotomies in the lateral wall of the maxilla .A 2,9 diameter burr is used to prepare de osteotomy at the level of the zygoma bone.
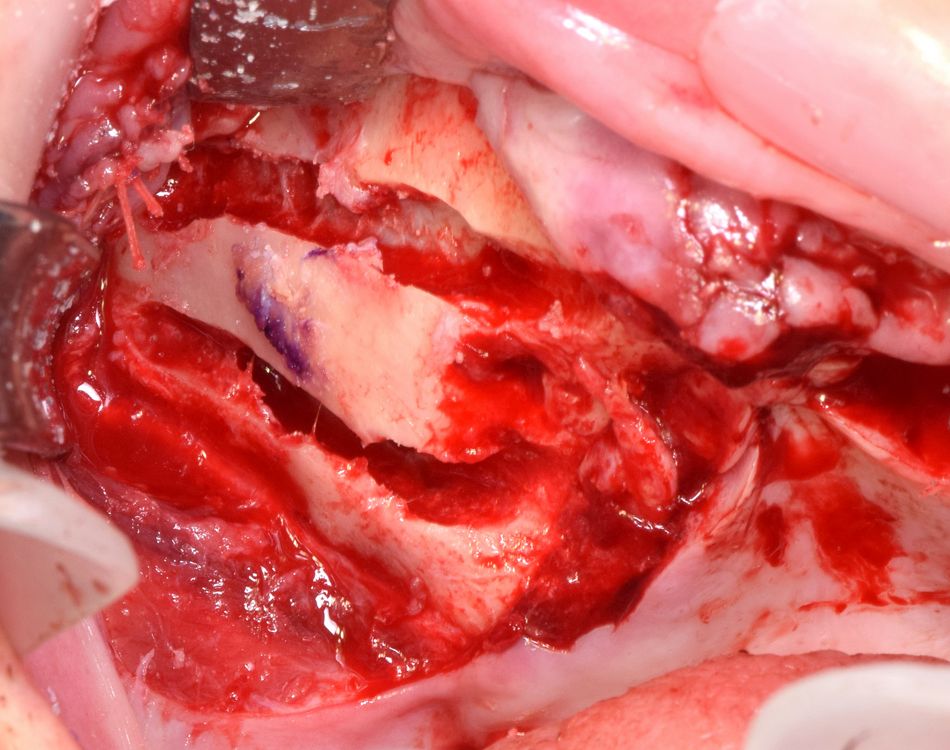
- Fig 13. Both implants in place.
Prosthetic procedure
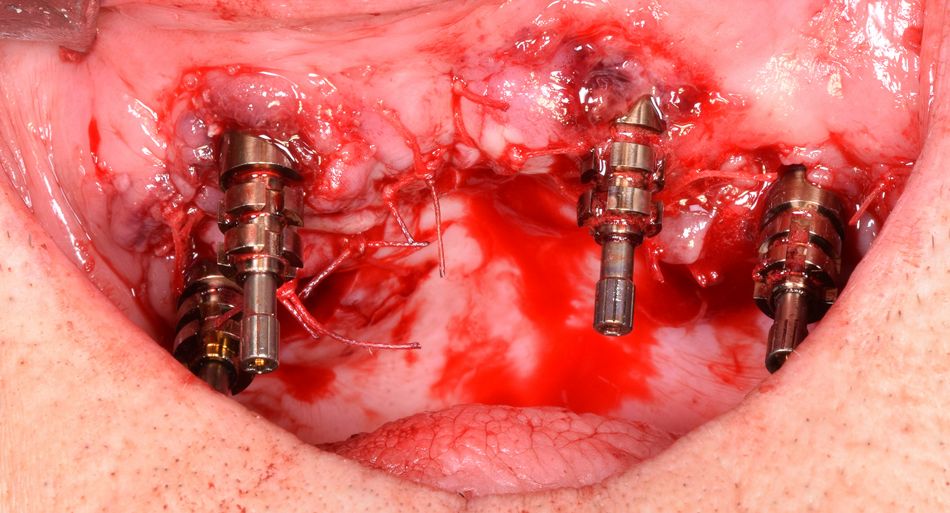
After insertion of the four implants (FIG. 14), multi-unit abutments (CH-SRA-4.5, Ex Hex, straight, diameter= 4.6 mm, GH= 4.5 mm) were placed to support the prosthetic rehabilitation. The flap was thoroughly adapted on the abutments, ensuring an excellent collar of keratinized tissue around the implants.
During the prosthetic phase, it was preferable for the patient to be fully conscious since impressions were taken only a few hours after surgery. Impressions can also be taken while the patient is still unconscious (under intravenous sedation or general anesthesia), but this will be more difficult and is not recommended.
- Fig 14. Four implants in place (2 Straumann Zygomatic implants Zaga round anteriorly and 2 Straumann Zygomatic implants Zaga flat posteriorly).
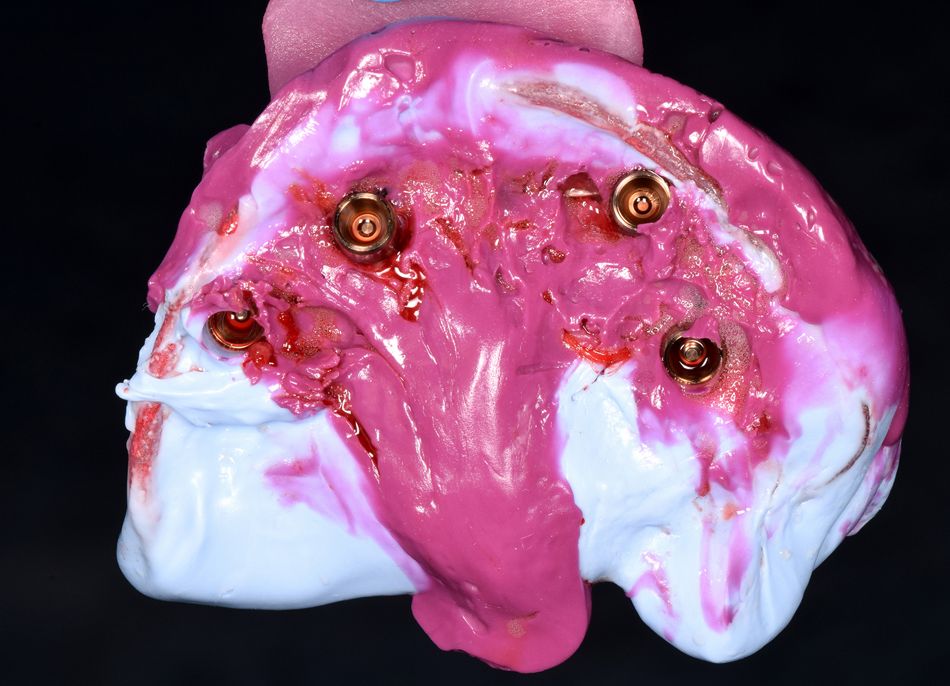
As a next step, impression copings were attached to the implant abutments (FIG. 15), and the transparent surgical guide was used for the impression transfer, placing and joining implants with acrylic resin. The same guide was used to register the patient’s occlusion and jaw relationship. Once the occlusion had been registered and the guide secured, the space between the impression copings and the surgical guide was filled with liquid silicone. As soon as the material hardened, the copings were removed together with the guide (FIG. 16), and the transepithelial abutments were covered with protective caps. The provisional prosthesis was fabricated in a conventional manner by casting a model and connecting laboratory analogs. If the patient already has a conventional denture that fulfills all the prosthetic requirements, this may be used as a guide for the surgical template and also for the conversion process to an all-acrylic bridge for immediate loading. The impression copings were picked up in the mouth. An impression was then made using an impression tray. The last implants were picked up on the model, and the intaglio surface was filled in.
- Fig 15. Impression copying in place
- Fig 16. Impression
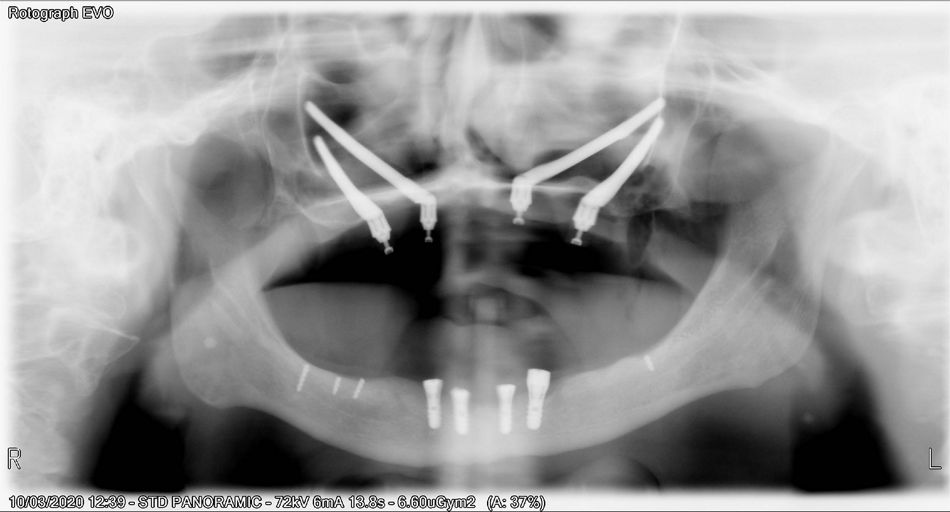
The postoperative radiograph confirmed the optimal positioning of the four zygomatic implants (FIG. 17).
The 1-month follow-up revealed optimal healing of the soft tissues (FIG. 18) under the provisional prosthesis (FIG. 19). After 4 months of healing, the final titanium-acrylic restoration was designed and delivered (FIG. 20).
- Fig 18. Intraoral view 1 month after surgery
- Fig 19. Provisional prosthesis in place (frontal view)
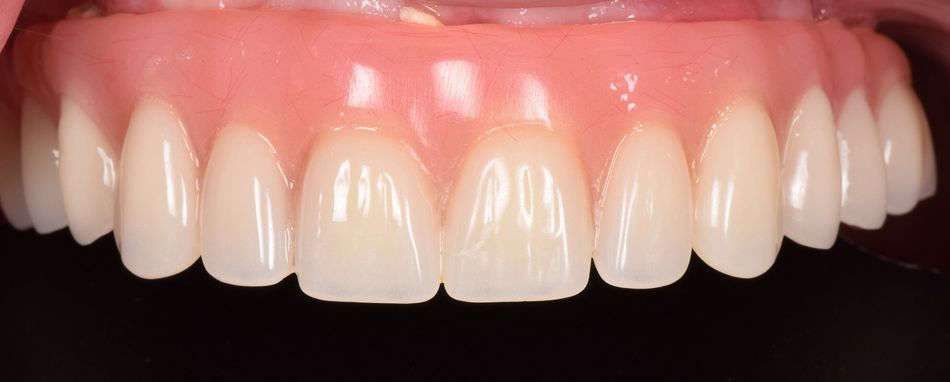
- Fig 20. Final prosthesis in place (frontal view)
Treatment outcomes
These outcomes were assessed at three different levels - patient, referrer and surgeon - as follows:
1. Patient
The patient expressed complete satisfaction from the functional, psychological and social perspectives. This was confirmed objectively by an OHIP 14 test (Oral Health Impact Profile) as an assessment of his quality of life, which reached level 1.4.
2. Referrer
The referrer expressed a high level of contentment due to the effectiveness of the surgical procedure in respecting synergistic interactions between surgeon and referrer. The initial expectations were all fulfilled even in this almost desperate clinical case where the quad zygoma procedure appeared from the outset to be the last option for this patient.
3. Surgeon
The surgeon valued the ease and efficiency of the implant handling, which promoted optimal soft tissue management and decreased surgery duration. The versatile design of the implants allows for anatomical and conservative placement. He expressed great confidence in the prognosis regarding the implant survival rate and the full rehabilitation success rate.
Quad zygoma procedure: Expert Opinion
- The insertion of four zygomatic implants (quad zygoma) is a first-line procedure for patients with very severe maxillary atrophy or possibly a rescue approach in patients with multiple implant failure.
- The zygoma anatomy-guided technique was introduced as a personalized surgical procedure in which the placement of the implants depends on the different anatomical features, special attention being paid to the curvature of the maxillo-zygoma complex.
- When properly inserted, the zygomatic implants guarantee adequate stability, allowing for immediate rehabilitation with a screw-retained bridge.
- A successful implementation of the quad zygoma technique requires advanced surgical skills and dedicated training.
References
- Davó R, Felice P, Pistilli R, et al. Immediately loaded zygomatic implants vs conventional dental implants in augmented atrophic maxillae: 1-year post-loading results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur J Oral Implantol 2018;11(2):145-61.
- Davó R, Pons O. 5-year outcome of cross-arch prostheses supported by four immediately loaded zygomatic implants: a prospective case series. Eur J Oral Implantol 2015;8(2):169-74.
- Davo R, David L. Quad zygoma: techniques and realities Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 31 (2019) 285–297
- Wang F, Monje A, Lin G, et al. Reliability of four zygomatic implant-supported prostheses for the rehabilitation of the atrophic maxilla: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2015;30(2):293-8.
- Van Steenberghe D, Malevez C, Van Cleynenbreugel J, et al. Accuracy of drilling guides for transfer from three-dimensional CT-based planning to placement of zygoma implants in human cadavers. Clin Oral Implants Res 2003;14:131–6